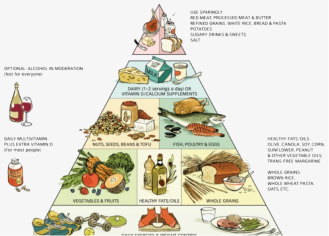
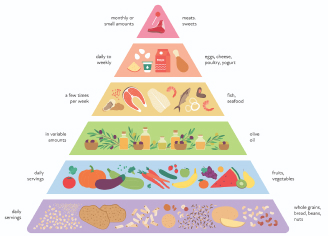
What is Paleo Diet?
The Paleo diet, short for the Paleolithic diet, is a dietary approach inspired by the eating habits of our ancient ancestors during the Paleolithic era, which dates back approximately 2.5 million to 10,000 years ago. The main idea behind the Paleo diet is to eat the way our hunter-gatherer ancestors did before the advent of agriculture. Advocates of this diet believe that our bodies are better adapted to the foods consumed during that era and that adopting a similar diet can lead to various health benefits.
Benefits
Weight Loss: The Paleo diet's emphasis on whole foods and higher protein intake may lead to increased satiety and reduced overall calorie consumption, which can support weight loss.
Improved Blood Sugar Control: By avoiding refined sugars and processed carbohydrates, the Paleo diet may help stabilize blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity.
Enhanced Nutrient Intake: The diet encourages the consumption of nutrient-dense foods like vegetables, fruits, and lean proteins, providing a wide array of essential vitamins and minerals.
Reduced Inflammation: The avoidance of processed foods and potential allergens like gluten and dairy may help reduce inflammation in some individuals.
Increased Energy and Focus: Some individuals report feeling more energetic and mentally alert when following the Paleo diet, possibly due to stable blood sugar levels and nutrient-rich foods.
Dos
- Meat: Grass-fed beef, poultry, pork, game meats.
- Seafood: Fish, shellfish, and other seafood.
- Eggs: Pasture-raised or free-range eggs.
- Vegetables: All types of non-starchy vegetables, including leafy greens, broccoli, cauliflower, carrots, etc.
- Fruits: Berries, apples, oranges, bananas, and other fruits in moderation.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, flaxseeds, etc.
- Healthy Fats: Avocado, coconut oil, olive oil, ghee (clarified butter).
Don'ts
- Grains: Wheat, barley, rice, oats, etc.
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, chickpeas, peanuts.
- Dairy: Milk, cheese, yogurt, butter.
- Refined Sugar: Added sugars, sugary beverages, desserts.
- Processed Foods: Processed snacks, packaged foods, and artificial ingredients.
Recipes
- Hanger Steak with Tahini and Smashed Charred Beets
- Eggs in Purgatory
- Blackened Carrots With Daikon and Pomegranates
- Tangy Vinegar Chicken With Barberries and Orange
- Tamarind-Glazed Black Bass With Coconut-Herb Salad
- Obe Ata Stew With Chicken and Spinach
- Crunchy Pickle Salad
- Turmeric Salmon With Coconut Crisp
- Collard Greens Salad With Fried Plantain and Sumac
- Saucy Chicken Puttanesca
For Images:
Was this article helpful?
Similar Articles